Principles Of Security | Try Hack Me |Jr Penetration Tester | By Mohit Damke
Principles Of Security | Try Hack Me |Jr Penetration Tester | By Mohit Damke

Introduction
The measures, frameworks and protocols discussed throughout this room all play a small part in "Defence in Depth."
Defence in Depth is the use of multiple varied layers of security to an organisation's systems and data in the hopes that multiple layers will provide redundancy in an organisation's security perimeter.
The CIA Triad
The CIA Triad represents three core principles of cybersecurity:
Confidentiality: Keep information private and accessible only to authorized users.
Integrity: Ensure data is accurate and unaltered by unauthorized individuals.
Availability: Keep systems and data accessible and operational when needed.
Confidentiality
Confidentiality means keeping information private and only accessible to those who are authorized. It ensures that sensitive data remains confidential and is not disclosed to unauthorized individuals or parties. Measures like encryption, access controls, and secure communication help maintain confidentiality and prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Privacy: Protecting information from unauthorized access.
Authorized Access: Only allowing approved individuals to view sensitive data.
Data Encryption: Encoding information so it's unreadable without a key.
Access Controls: Setting permissions for who can access specific data.
Secure Transmission: Ensuring data is safe during communication.
Non-Disclosure: Not sharing confidential information with unauthorized parties.
Integrity
Data Accuracy: Ensuring information remains accurate and trustworthy.
Preventing Tampering: Protecting data from unauthorized changes.
Checksums and Hashing: Using techniques to detect alterations in data.
Version Control: Managing and tracking changes to prevent unauthorized modifications.
Digital Signatures: Adding electronic signatures to verify the authenticity of data.
Audit Trails: Keeping records of changes made to data for accountability.
Data Validation: Checking data inputs to ensure they meet expected standards.
Availability
Always Accessible: Ensuring data and systems are available when needed.
Downtime Prevention: Preventing disruptions that could lead to unavailability.
Redundancy: Having backup systems to ensure continuous operation.
Load Balancing: Distributing workloads to avoid overloading systems.
Disaster Recovery: Having plans to restore functionality after incidents.
Distributed Architecture: Spreading services across multiple locations for resilience.
Network Monitoring: Keeping an eye on systems to identify and fix issues quickly.
Service Level Agreements (SLAs): Commitments to maintain specific levels of availability.
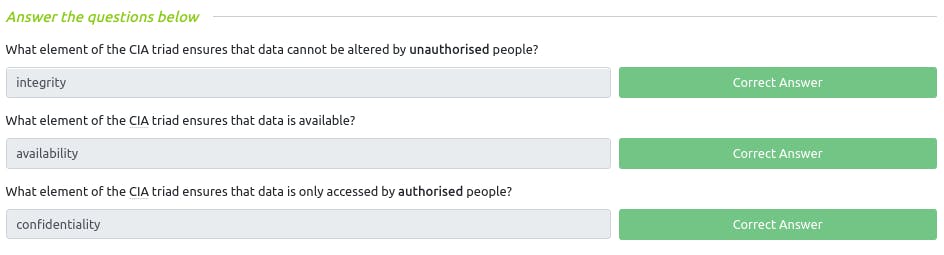
Q : What element of the CIA triad ensures that data cannot be altered by unauthorized
~ Integrity
Q : What element of the CIA triad ensures that data is available?
~ Availability
Q : What element of the CIA triad ensures that data is only accessed by authorised people?
~ Confidentiality
Principles of Privileges

The levels of access given to individuals are determined on two primary factors:
The individual's role/function within the organisation
The sensitivity of the information being stored on the system
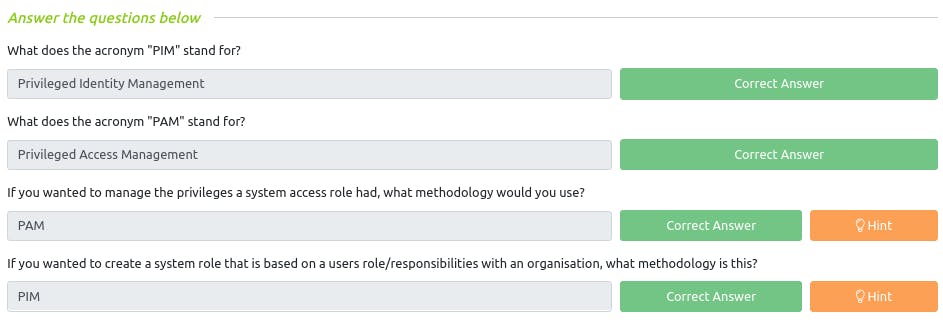
Q : What does the acronym "PIM" stand for?
~ Privileged Identity Management
Q : What does the acronym "PAM" stand for?
~ Privileged Access Management
Q : If you wanted to manage the privileges a system access role had, what methodology would you use?
~ PAM
Q : If you wanted to create a system role that is based on a users role/responsibilities with an organisation, what methodology is this?
~ PIM
Security Models Continued
The Bell-La Padula Model

Biba Model
![Information Security Series: [Part2] Principles of Privileges](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1647290923282/j6dpvF48i.png?auto=compress,format&format=webp&auto=compress,format&format=webp)
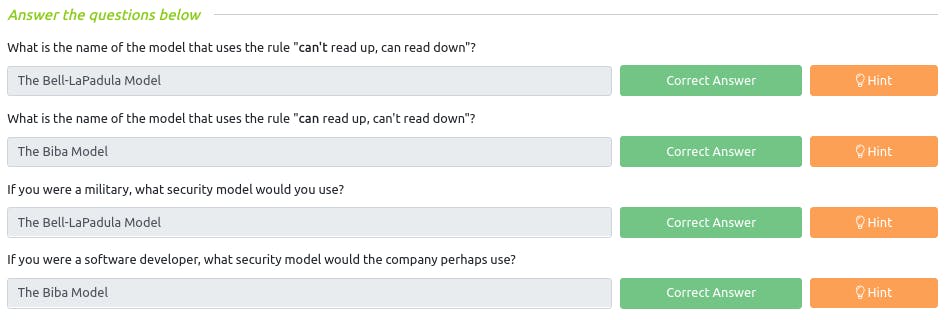
Q : What is the name of the model that uses the rule "can't read up, can read down"?
~ The Bell-LaPadula Model
Q : What is the name of the model that uses the rule "can read up, can't read down"?
~ The Biba Model
Q : If you were a military, what security model would you use?
~ The Bell-LaPadula Model
Q : If you were a software developer, what security model would the company perhaps use?
~ The Biba Model
Threat Modelling & Incident Response

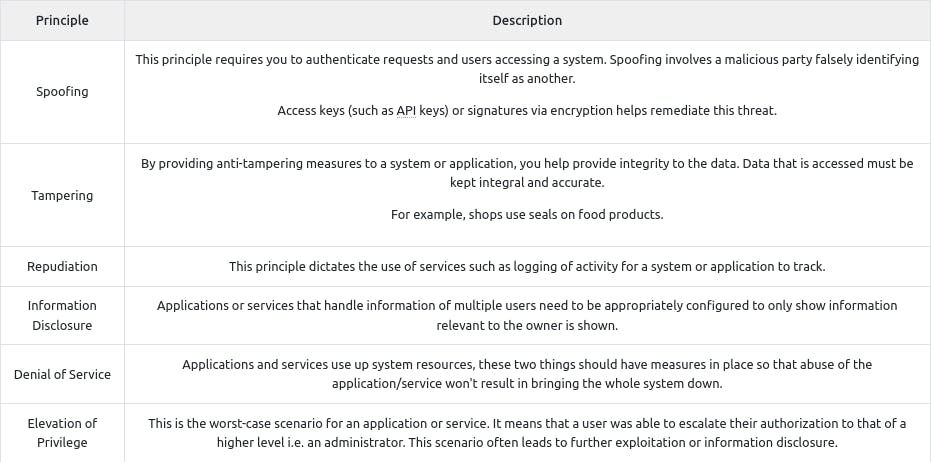
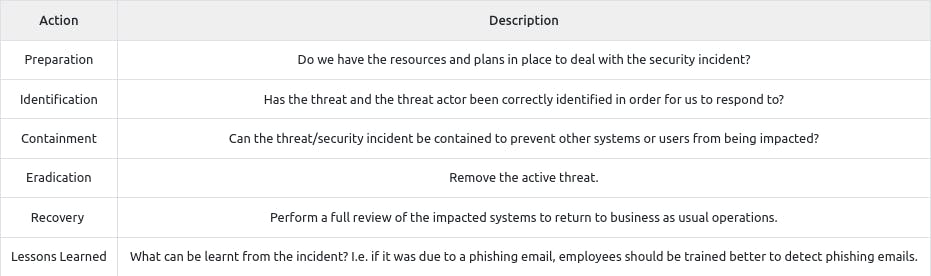
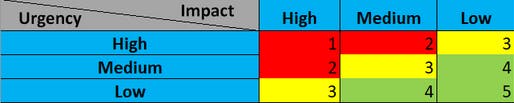
Q : What model outlines "Spoofing"?
~ STRIDE
Q : What does the acronym "IR" stand for?
~ Incident Response
Q : You are tasked with adding some measures to an application to improve the integrity of data, what STRIDE principle is this?
~ Tampering
Q : An attacker has penetrated your organisation's security and stolen data. It is your task to return the organisation to business as usual. What incident response stage is this?
~ Recovery